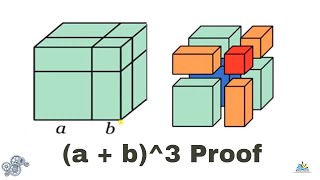
(a+b)^3 geometric proof 316253-(a+b)^3 geometric proof
An axiom is a mathematical statement that is accepted without proof Euclidean geometry starts with undefined terms and a set of postulates and axioms For example, the following statement is an axiom of Euclidean geometry Use the results from part (3) to prove that 8 divides (\(a b 2\)) Write a proof for Proposition 35 Answer AddIntegers hard (11 MiB, 5,550 hitsOpposite sides are congruent b Yes;

Nice Geometric Parallelepiped Proof Mathematics Stack Exchange
(a+b)^3 geometric proof
(a+b)^3 geometric proof-Vectors measurement of angles (4903 KiB, 6,560 hits);View geometric proofs BONUS ASSIGNMENTpdf from MAC 2311 at Everglades High School Name _ Date _ Class_ LESSON 26 Practice B Geometric Proof Write a justification for each step Given AB = EF, B



Fermat S Last Theorem Thinking About Geometry Underground Mathematics
In this section we will define the dot product of two vectors We give some of the basic properties of dot products and define orthogonal vectors and show how to use the dot product to determine if two vectors are orthogonal We also discuss finding vector projections and direction cosines in this sectionGeometric Properties of the Dot Product Length and Distance Formula For A = (a 1, a 2, , a n), the dot product A A is simply the sum of squares of each entry In the plane or 3space, the Pythagorean theorem tells us that the distance from O to A, which we think of as the length of vector OA, (or just length of A), is the square root of this numberFor (a b)^3 watch http//youtube/3HPyrM4kYhk a^3 b^3 watch http//youtube/5x4gJPchSiY a^3 b^3 watch http//youtube/9RHJt0GXLcY It is very easy
Connecting Algebra & Geometry using Coordinates 55 NApplications and Proofs with Coordinates ame Areas 1 Find the area of the rectangles shown in each graph below A B 2 Find the area of the triangles shown in each graph below A BGeometry Unit 3 Congruence and Proof Reflexive Property Symmetric Property Transitive Property Parallel Lines AB = AB If a = b, then b = a If a=b and b=c, then a=c lines in the same plane that never intersect Reflexive Property AB = AB Symmetric Property If a = b, then b = a 68 terms WarrenMathThe arithmetic meangeometric mean (AMGM) inequality states that the arithmetic mean of nonnegative real numbers is greater than or equal to the geometric mean of the same list Further, equality holds if and only if every number in the list is the same Mathematically, for a collection of
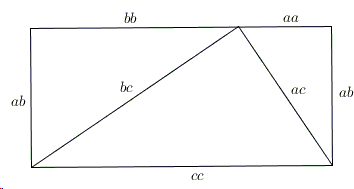
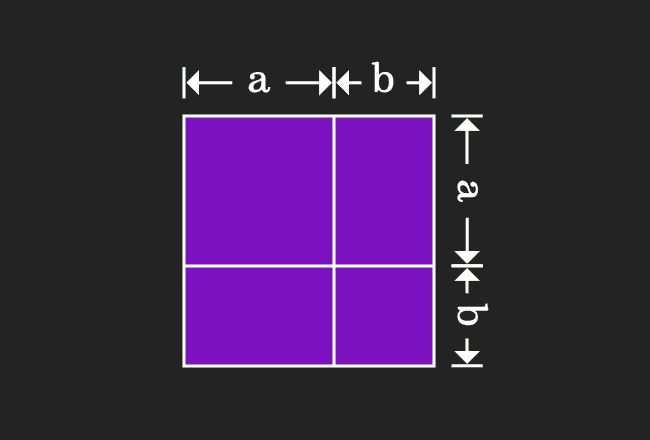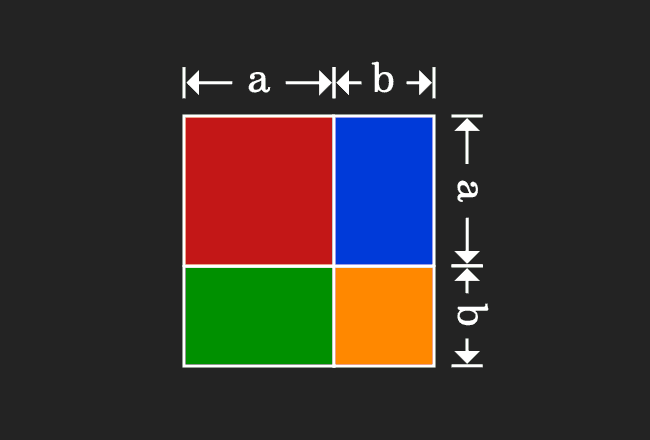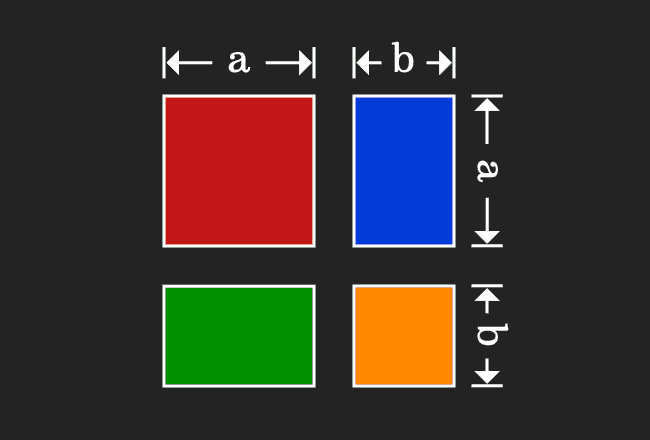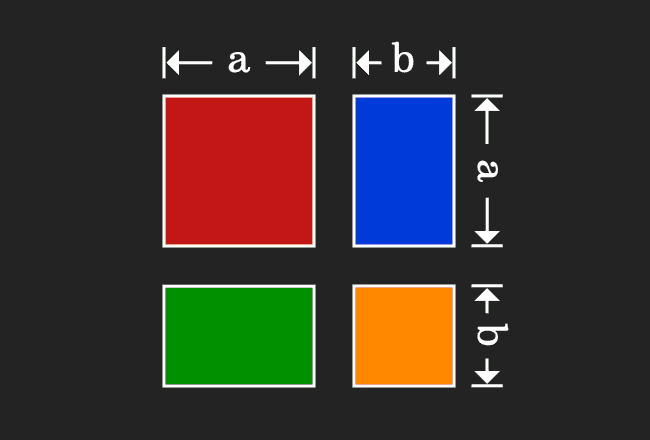
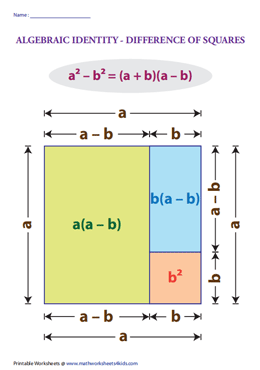
For positive values of a and b, the binomial theorem with n = 2 is the geometrically evident fact that a square of side a b can be cut into a square of side a, a square of side b, and two rectangles with sides a and bWith n = 3, the theorem states that a cube of side a b can be cut into a cube of side a, a cube of side b, three a × a × b rectangular boxes, and three a × b × b\(=> a^3 – b^3 = (ab)((ab)^2 3ab) \) use the formula of a minus b whole square \(=> a^3 – b^3 = (ab)(a^2 b^2 2ab 3ab) \) \(=> a^3 – b^3 = (ab)(a^2 b^2 ab) \) Proof Formula \( a^3 – b^3 = (ab)(a^2 b^2 ab) \) Verify \( a^3 – b^3 \) FormulaYou cannot prove that the quadrilateral is a Geometry Help!



Fermat S Last Theorem Thinking About Geometry Underground Mathematics



Write The Geometrical Proof Of A B 3 Brainly In
Geometric proofs are so beautiful here's a little Blender project to visualize the expansion of a cubed sum of numbers#physics #education #math1 (a b)2 = a2 2ab b2 2 (a b)2 = a2 2ab b2 3 (a b)3 = a3 b3 3ab(a b) 4 (a b)3 = a3 b3 3ab(a b) 5 (a b c)2 = a2 b2 c2 2ab2bcAnd write proofs a) Triangles b) Quadrilaterals c) Other polygons d) Circles 4 Develop and apply properties of solids to solve problems GOAL 3 The learner will transform geometric figures in the coordinate plane algebraically 301 Describe the transformation (translation, reflection, rotation, dilation) of polygons in the



Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Brilliant Math Science Wiki



A B 3 Geometrical Proof Youtube
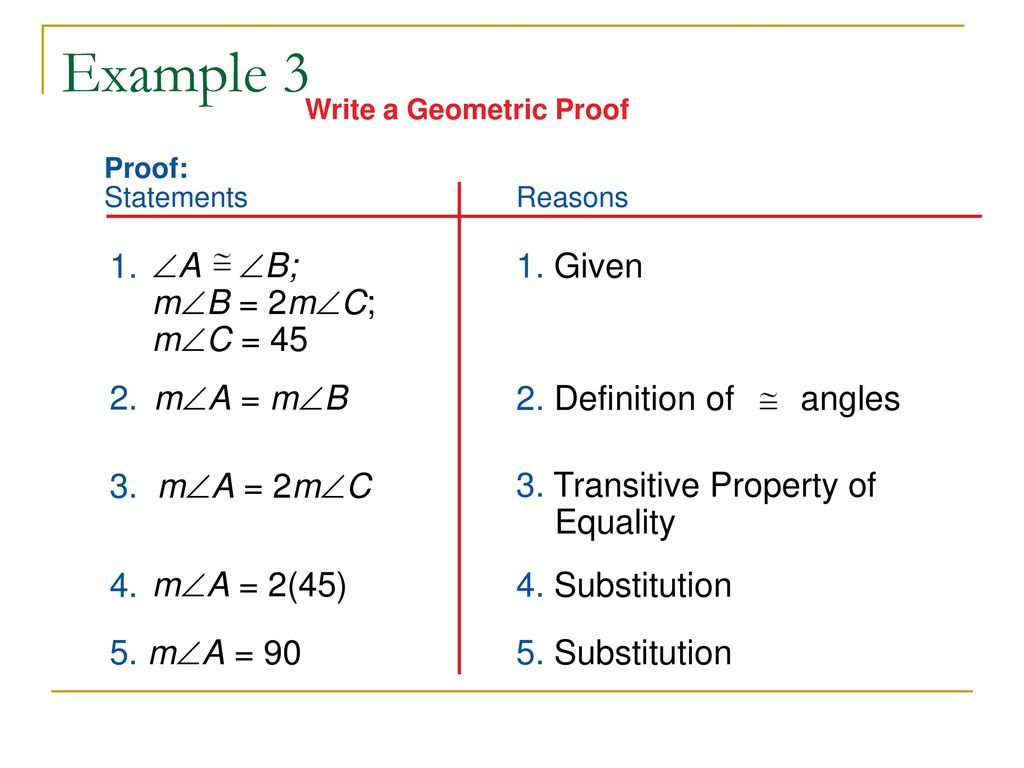
Proofs Proofs are step by step reasons that can be used to analyze a conjecture and verify conclusions In a formal proof, statements are made with reasons explaining the statements You begin by stating all the information given, and then build the proof through steps that are supported with definitions, properties, postulates, and theoremsProve that if y 3 3 y − 4 = 6 \frac{y}{3} 3y4=6 3 y 3 y − 4 = 6, then y = 3 y=3 y = 3 Use the two columnproof method Use the two columnproof method Algebraic proofs1 Assume that √2 is a rational number, meaning that there exists an integer a and an integer b in general such that a / b = √2 2 Then √2 can be written as an irreducible fraction a / b such that a and b are coprime integers and (a / b)2 = 2 3 It follows that a2 / b2 = 2 and a2 = 2 b2 ( (a / b)n = an / bn ) 4



Euclidean Geometry Plane Geometry Britannica



Holt Geometry 2 6 Geometric Proof Warm Up Determine Whether Each Statement Is True Or False If False Give A Counterexample 1 It Two Angles Are Complementary Ppt Download
Learn geometry proofs with free interactive flashcards Choose from 500 different sets of geometry proofs flashcards on QuizletGeometric Proofs Proving Triangles Congruent LET'S GET STARTED Before we begin, let's see how much you already know In your print materials there is a EntryTest Complete it now CHECK YOURSELF SECTION 1 1 AC AB 2 C B 3Geometry Based on the information in the diagram, can you prove that the figure is a parallelogram?



Mathematics Visualization Tumblr Posts Tumbral Com



Binomial Theorem
HJ is the bisector of IHK and 1 3 1 __› HJ is the bisector of IHK B A Definition of bisector 2 2 1 A B Given 3 1 3 B C Transitive Prop of 4 2 3 C 5 In a twocolumn proof, each step in the proof is on the left and the reason for the step is on the rightGeometry Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e In Exercises 27 to 30, fill in the missing reasons for each geometric proof Given B D → bisects ∠ A B C Prove m ∠ A B D = 1 2 ( m ∠ A B C ) Exercises 29, 30 PROOF Statements Reasons 1Prove that if y 3 3 y − 4 = 6 \frac{y}{3} 3y4=6 3 y 3 y − 4 = 6, then y = 3 y=3 y = 3 Use the two columnproof method Use the two columnproof method Algebraic proofs


Pythagorean Theorem And Its Many Proofs



Yismxplusc Geometric Proof Of The Cubic Formula A B 3
CHECK YOURSELF SECTION 1 1 CONGRATULATIONS You have officially completed this module on proofs!!!!Just like we expressed the geometric proof of expansion of quadratic formula we prove the expansion of (a b)3 the expansion is (ab)³ = a³ 3a²b 3ab² b³ PROOF Lets draw a cube with side length (ab) , hence we know that the volume of this cube would be equal to (a b)3Most downloaded worksheets Ones to thousands (845 KiB, 8,256 hits);


The Algebraic And Geometric Proofs Of Pythagorean Theorem



Will Give Brainliest Consider The Two Column Geometric Proof Below A Fill In The Brainly Com
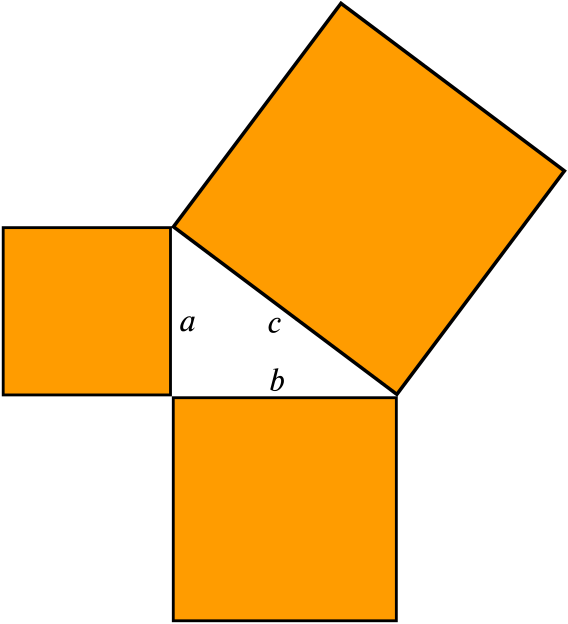
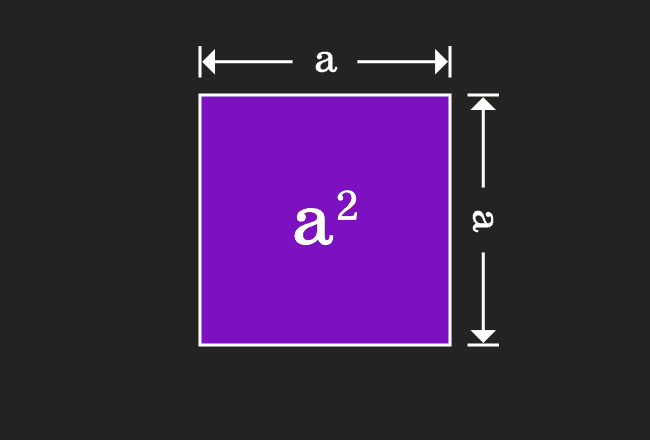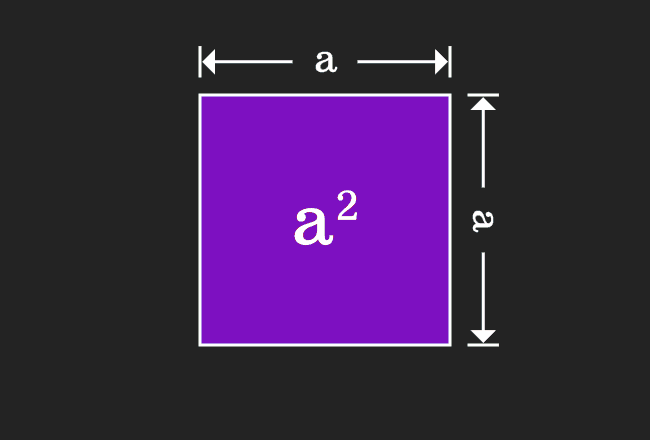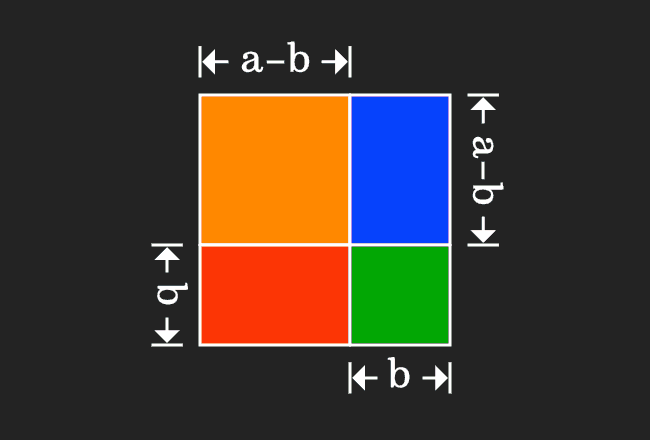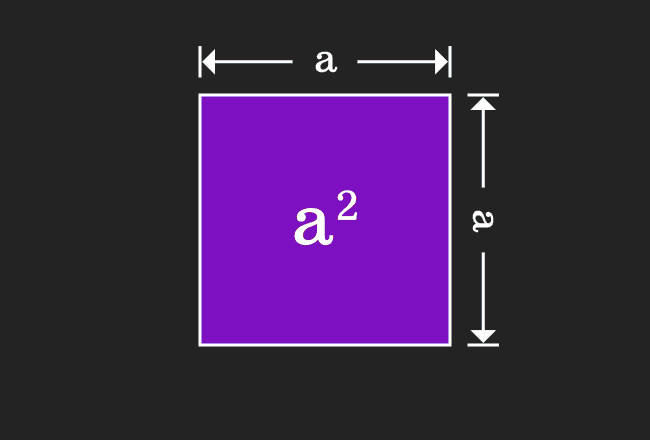
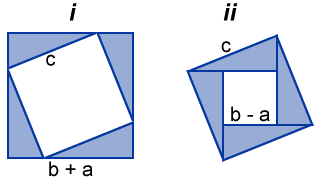
Informal Proof 1 2 3 — 180 Add parallel line to one of the sides A 1 B = 180 degrees (straight angle and addition postulate) A = 2 and B = 3 (parallel lines cut by transversal, then alt interior angles are congruent) — 180 degrees (substitution)A geometry proof — like any mathematical proof — is an argument that begins with known facts, proceeds from there through a series of logical deductions, and ends with the thing you're trying to prove Geometry proofs follow a series of intermediate conclusions that lead to a final conclusion Beginning with some given facts, sayThe algebraic identities $(ab)c \equiv a c b c$ and $(ab)^2 \equiv a^2 2a b b^2$ can be justified by pictures, as Figures 1 and 2 show
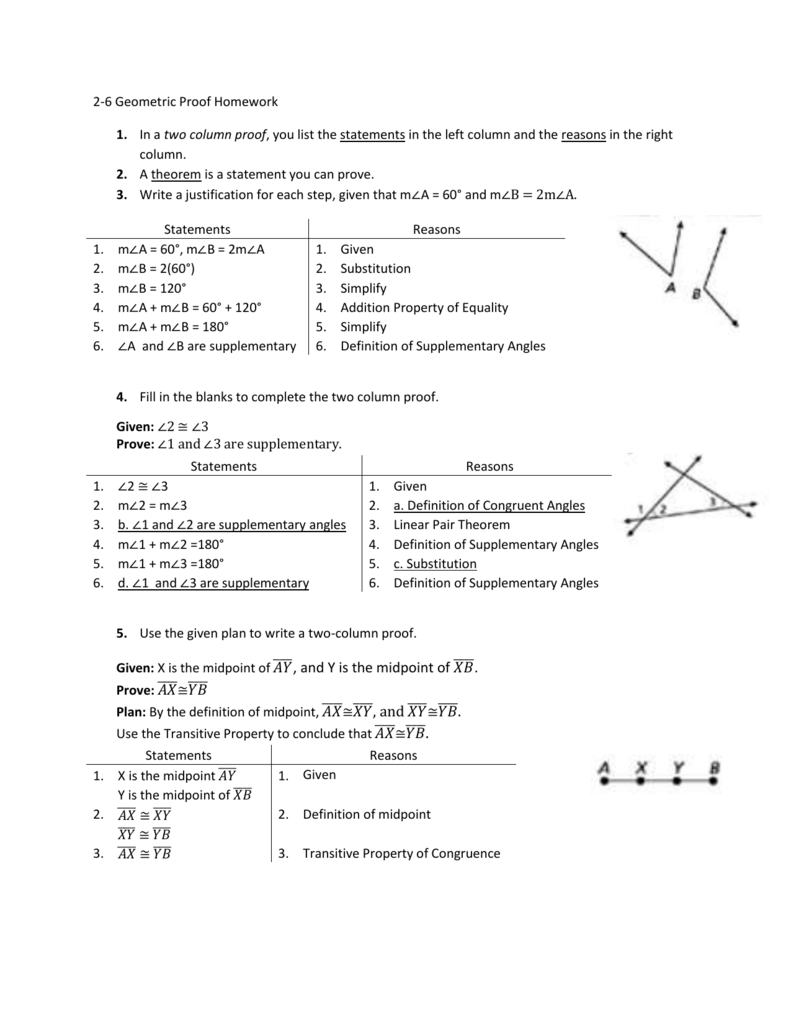


2 6 Geometric Proof Homework In A Two Column Proof You List The



Two Column Proofs Triangles Medians And Altitudes Youtube
A geometric proof uses reasoning to create a chain of logical steps that move from the hypothesis to the conclusion Proof Process 1 Draw a diagram to represent the statement to be proven 3 State the given information in terms of the diagram and mark it on the diagramStack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeAnd write proofs a) Triangles b) Quadrilaterals c) Other polygons d) Circles 4 Develop and apply properties of solids to solve problems GOAL 3 The learner will transform geometric figures in the coordinate plane algebraically 301 Describe the transformation (translation, reflection, rotation, dilation) of polygons in the


Pythagorean Theorem Calculator


2
For positive values of a and b, the binomial theorem with n = 2 is the geometrically evident fact that a square of side a b can be cut into a square of side a, a square of side b, and two rectangles with sides a and bWith n = 3, the theorem states that a cube of side a b can be cut into a cube of side a, a cube of side b, three a × a × b rectangular boxes, and three a × b × bGeometric Properties of the Dot Product Length and Distance Formula For A = (a 1, a 2, , a n), the dot product A A is simply the sum of squares of each entry In the plane or 3space, the Pythagorean theorem tells us that the distance from O to A, which we think of as the length of vector OA, (or just length of A), is the square root of this numberDot product and vector projections (Sect 123) I Two definitions for the dot product I Geometric definition of dot product I Orthogonal vectors I Dot product and orthogonal projections I Properties of the dot product I Dot product in vector components I Scalar and vector projection formulas There are two main ways to introduce the dot product Geometrical


A B 3 I E A Plus B Cube Formula Proof Ntse Algebraic Formulas Identity Geometrically Youtube


Proof Of A B Formula In Geometric Method
The respective spiral similarities are A(√ 3,30°) and B(√ 3,30°) That implies MN = LN and the angle between them must be 60° There are in fact many proofs of the theorem's statement, including a synthetic (coordinatefree) one, a trigonometric one, a symmetrybased approach, and proofs using complex numbers BackgroundOpposite angles are congruent c No;Connecting Algebra & Geometry using Coordinates 55 NApplications and Proofs with Coordinates ame Areas 1 Find the area of the rectangles shown in each graph below A B 2 Find the area of the triangles shown in each graph below A B


Geometry Summary Angles


Schools Pgcps Org Marchenrichment Content Geometry Answer Key
A 3 b 3 c 3 − 3abc = (a b c) (a 2 b 2 c 2 − ab − bc − ac) If (a b c) = 0, a 3 b 3 c 3 = 3abc Some not so Common Formulas Power n Formula a n − b n = (a − b) (a nMost downloaded worksheets Ones to thousands (845 KiB, 8,256 hits);Day 4 – Practice writing Coordinate Geometry Proofs 1 The vertices of ABC are A(3,3), B(5,3) and C(1,1) Prove by coordinate geometry that ABC is an isosceles right triangle 2 Given ABC with vertices A(4,2), B(4,4) and C(2,6), the midpoints of AB and BC are P and Q, respectively, and PQ is drawn Prove by coordinate geometry a PQ



Yismxplusc Geometric Proof Of The Cubic Formula A B 3


Proof Of A B Formula In Geometric Method
Learn ch geometry proofs chapter 3 with free interactive flashcards Choose from 500 different sets of ch geometry proofs chapter 3 flashcards on QuizletInformal Proof 1 2 3 — 180 Add parallel line to one of the sides A 1 B = 180 degrees (straight angle and addition postulate) A = 2 and B = 3 (parallel lines cut by transversal, then alt interior angles are congruent) — 180 degrees (substitution)Vectors measurement of angles (4903 KiB, 6,560 hits);


Pythagorean Theorem Calculator


Algebraic Identities Charts Printable Formulas
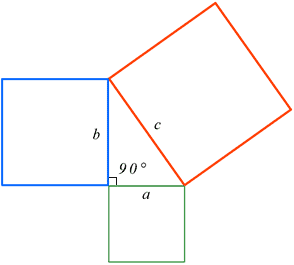
Give a geometric proof of the AMGM inequality For the next two problems you need to remember the Pythagorean theorem If a, b, and c are the side lengths of a right triangle and c is the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle, then a2 b2 = c2Geometric vectors A vector describes a movement from one point to another Vector notation A vector quantity has both direction and magnitude 3 \(e b a\) Reveal answer 1 \(e\)$\begingroup$ You have two squares of side a and b There are only 3 general types of squares as shown in the diagram (3 remainders side leaving remainder 1, 2 or 0 on division by 3 ) Now, you say that both the given square (a^2 & b^2) are of type 1 and their sum (a^2 b^2) is another square (c^2) ?



A B 3 Geometric Proof 3d Visual A B Whole Cube Formula A Model Bangla Math Language Youtube
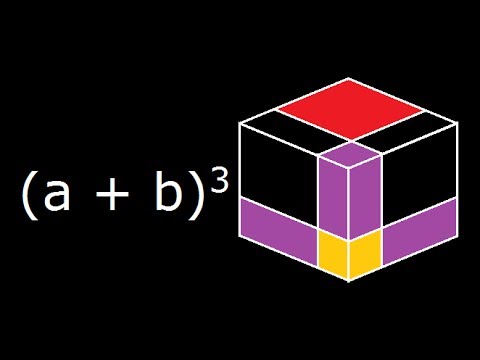


A B 3 A Plus B Cube Algebra Identity Geometrical Explanation And Derivation Youtube
The following is a statement I have been trying to prove (while solving problem 1426 in Algorithms (4th edition) by Robert Sedgewick) Show that three points $(a, a^3), (b, b^3), and (c, c^3)Informal Proof 1 2 3 — 180 Add parallel line to one of the sides A 1 B = 180 degrees (straight angle and addition postulate) A = 2 and B = 3 (parallel lines cut by transversal, then alt interior angles are congruent) — 180 degrees (substitution)Integers hard (11 MiB, 5,550 hits



Pythagorean Theorem From Wolfram Mathworld



Pythagorean Theorem Definition History Britannica
I'm so confused ( 1 Supply the missing reasons to complete the proof1 Assume that √2 is a rational number, meaning that there exists an integer a and an integer b in general such that a / b = √2 2 Then √2 can be written as an irreducible fraction a / b such that a and b are coprime integers and (a / b)2 = 2 3 It follows that a2 / b2 = 2 and a2 = 2 b2 ( (a / b)n = an / bn ) 4A geometric inequality for cyclic quadrilaterals 143 case If (iii), then we must show √ 2 cos π 4 − c 2 cos b 2 ≥cosbcosc1, where bc= π/2, ie, 2cos b 2 ≥ 1 √ 2 (sinbcosb1)=sin b π 4 1 √ 2, 0 ≤b≤π/2 The last inequality follows from observing that the function k(b)=2cos b


Chapter 2 6 Algebraic Proof Ppt Download
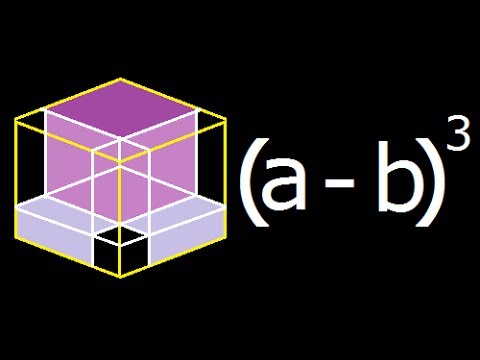


A Minus B Cube Or A Minus B Whole Cube A B 3 Geometric Explanation Derivation Youtube
The respective spiral similarities are A(√ 3,30°) and B(√ 3,30°) That implies MN = LN and the angle between them must be 60° There are in fact many proofs of the theorem's statement, including a synthetic (coordinatefree) one, a trigonometric one, a symmetrybased approach, and proofs using complex numbers BackgroundThe above problem which is actually a reformulation of Hlawka's inequality has been published in the popular Russian magazine Kvant as Problem M394 with the solution by Yu Ionin (Kvant, 1977, 03, p 32)Since $\vec{d}=\vec{a}\vec{b}\vec{c}\,$ and, eg, $\vec{d}\vec{a}=\vec{b}\vec{c},\,$ the above inequality is equivalent to Hlawka's



Math 2 Geometry Based On Elementary Geometry 3 Rd Ed By Alexander Koeberlein 1 5 Introduction To Geometric Proof Ppt Download



Art Of Problem Solving
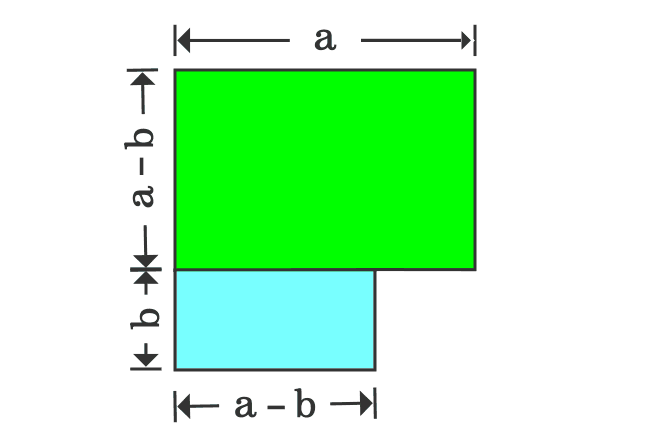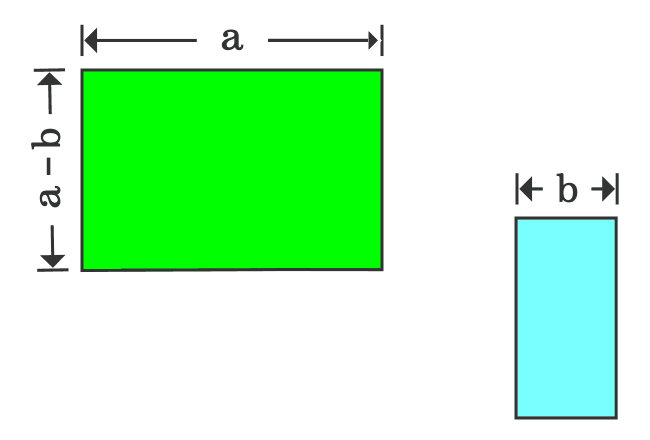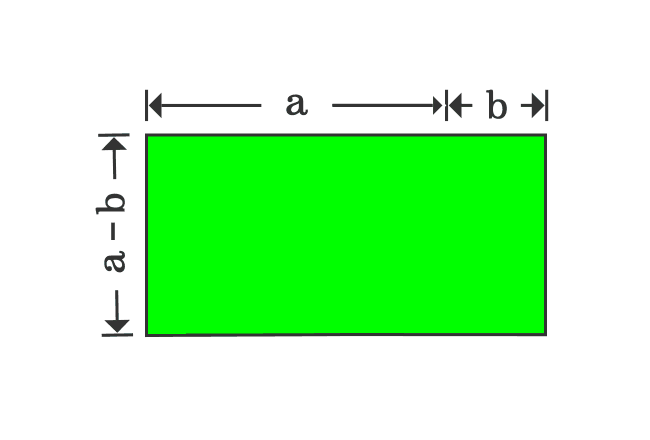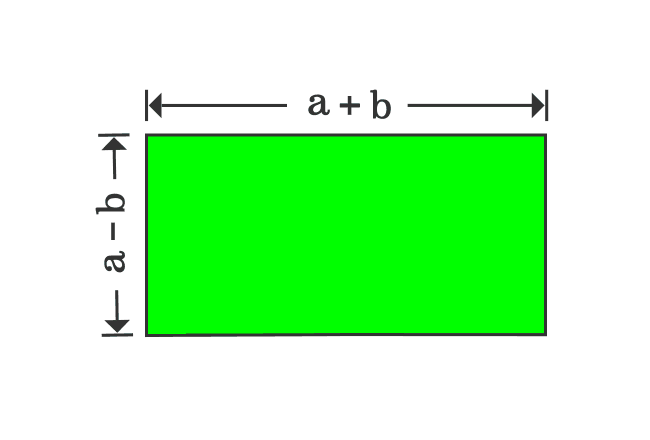


Proof Of A B Formula In Geometric Method
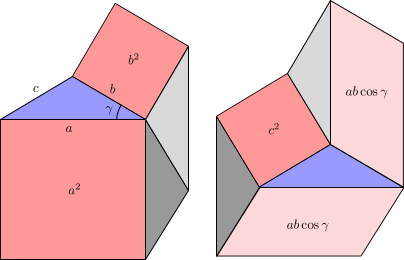


Law Of Cosines Wikipedia



Squared Triangular Number Wikipedia
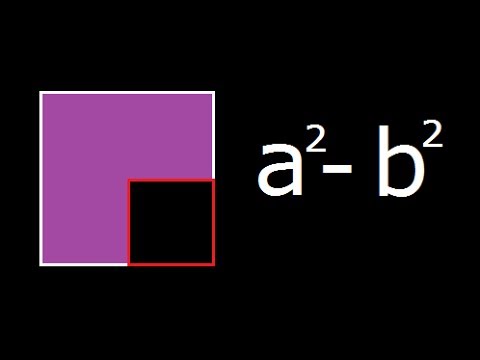


A Square Minus B Square A 2 B 2 Geometrical Explanation And Derivation Youtube


Geometry Proofs Wikiversity
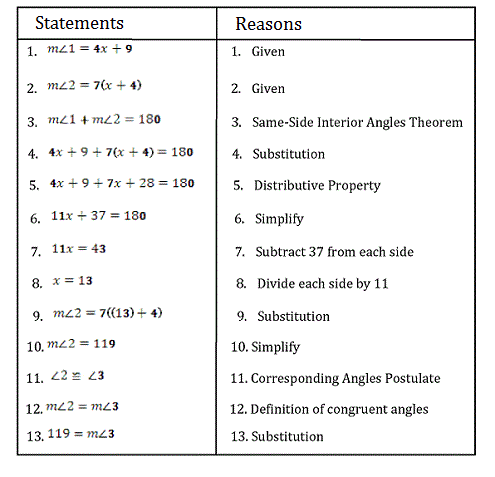


Angle Properties Postulates And Theorems Wyzant Resources


Q Tbn And9gcr3ixhshawibrcxd6oncuv0lei0pabfr1ixclntl0v Gzphb Hn Usqp Cau
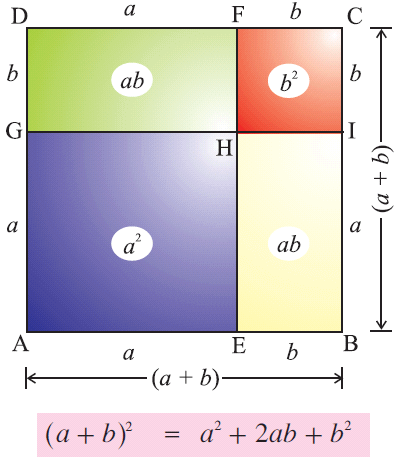


Algebraic Identities


Classroom Geometry Proofs Of Perimeter And Area For Geometric Figures Video Math Teacher


Illustrations Of Formulas



Shoelace Formula Wikipedia


Using The Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Inequality In Problem Solving
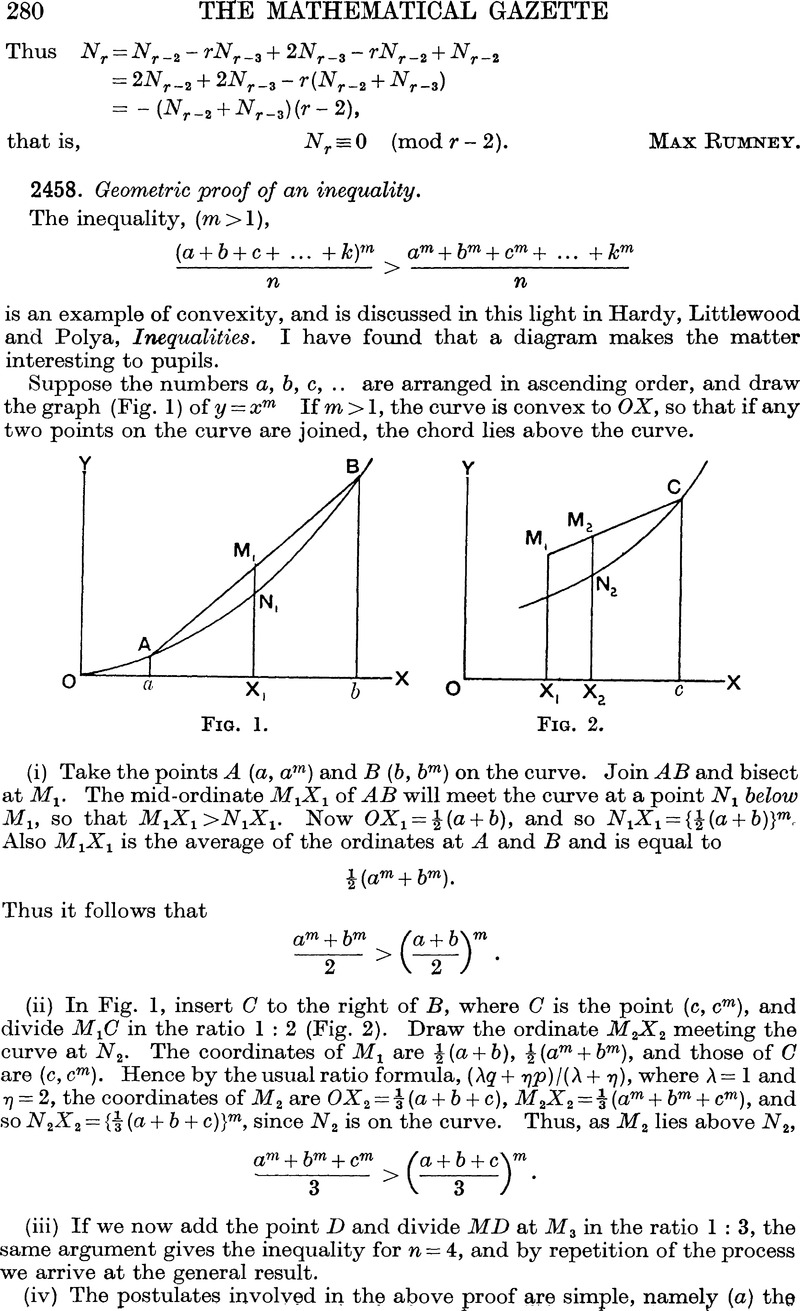


2458 Geometric Proof Of An Inequality The Mathematical Gazette Cambridge Core



What Are Tips For Writing Geometry Proofs Quora
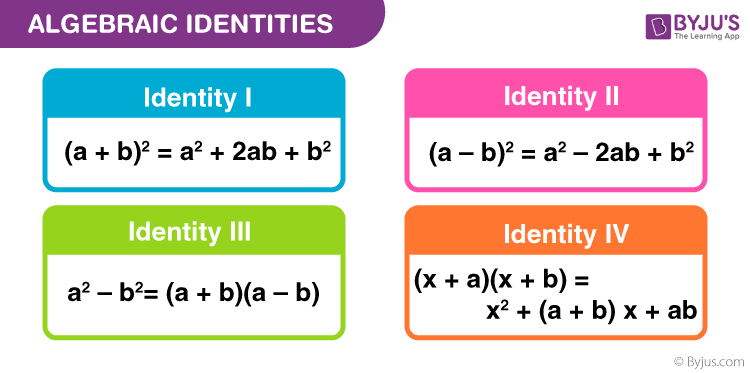


Algebraic Identities Standard Algebraic Identities Definition Examples



Geometry Proof Definition Of Midpoint Payment Proof



Algebraic Identities Proofs Solved Examples Practice Questions



Nice Geometric Parallelepiped Proof Mathematics Stack Exchange


Search Q A 5e3 2bb 5e3 Formula Proof Tbm Isch


The Algebraic And Geometric Proofs Of Pythagorean Theorem
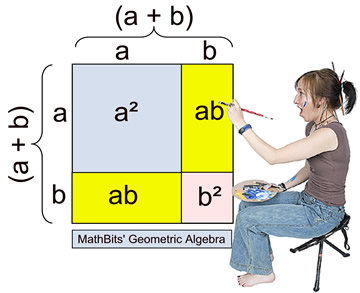


Special Binomial Patterns Mathbitsnotebook A1 Ccss Math


Www Amphi Com Cms Lib Az Centricity Domain 256 2 6 7 geometric proof Pdf
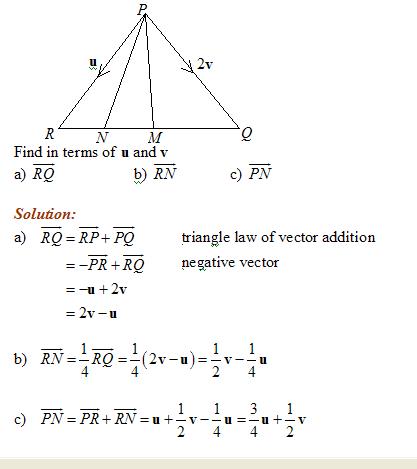


Vector Geometry Solutions Examples Videos



3 2 7 A B C D E These Are Easy Proofs Do Chegg Com



A Cube Plus B Cube A 3 B 3 Geometrical Explanation And Derivation Of Algebra Identity Youtube


Q Tbn And9gcr3ixhshawibrcxd6oncuv0lei0pabfr1ixclntl0v Gzphb Hn Usqp Cau



Algebraic Identities Proofs Solved Examples Practice Questions



Aren T Infinite Geometric Series Cool If You Just Shouted Yes Then You Are Potentially As Geeky As I Am A Proof Without Math Methods Education Math Math
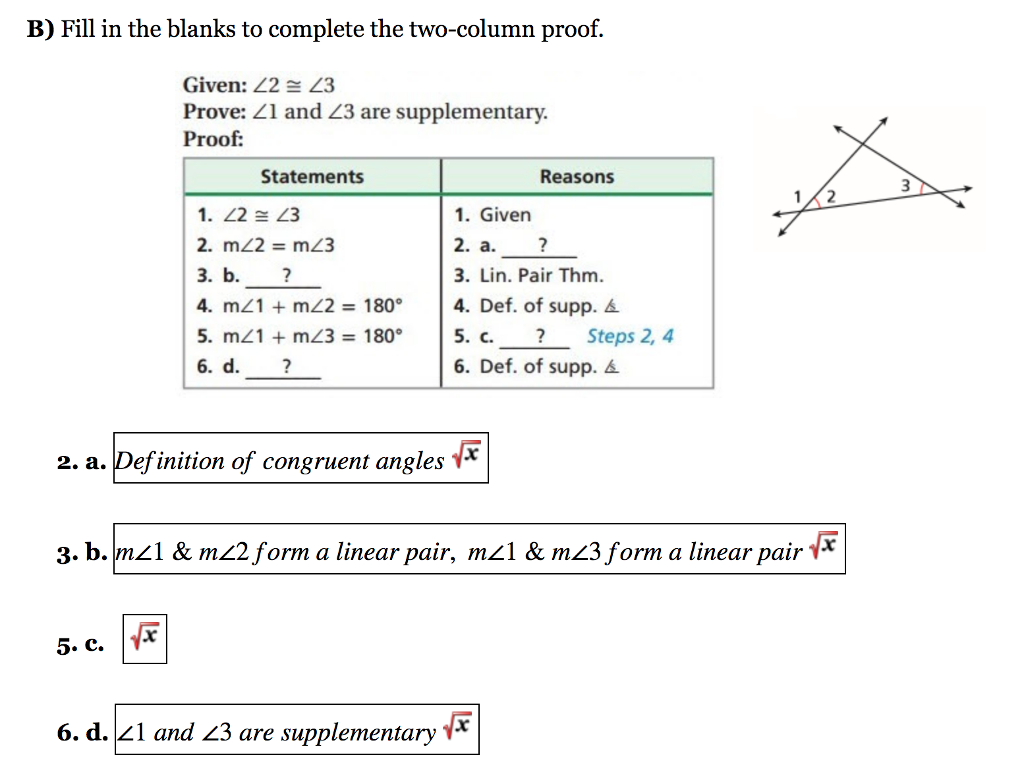


Proof Definition Of Congruent Angles Payment Proof



Hai Can U Give Me The Geometrical Proof For A B 3and A B 3 Math Meritnation Com



A B 3 Geometric Proof
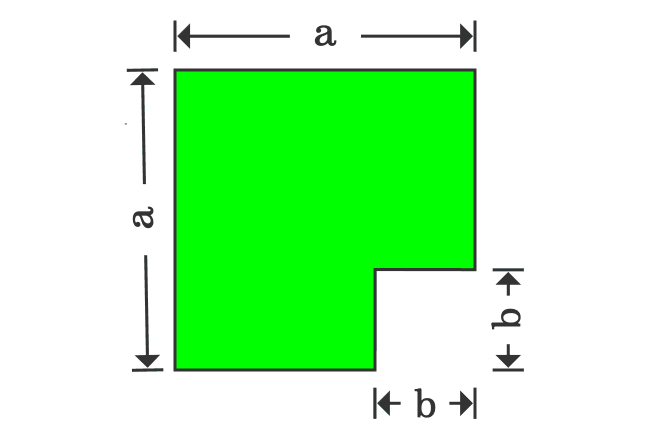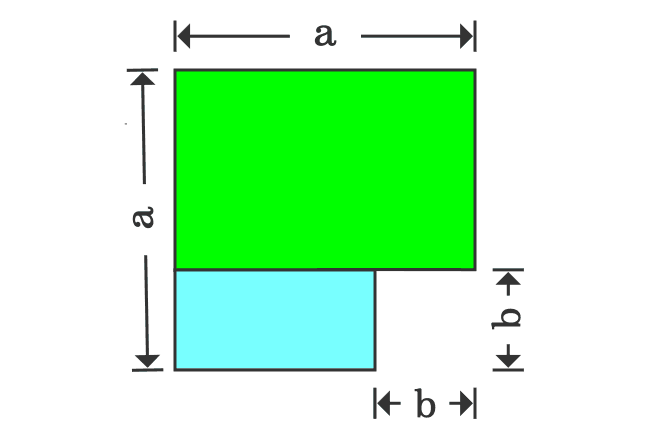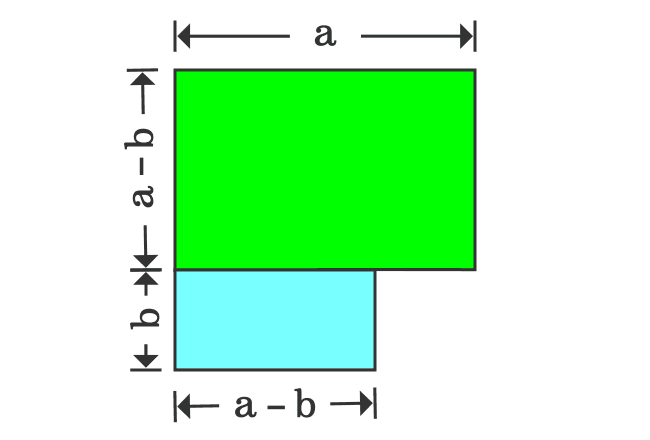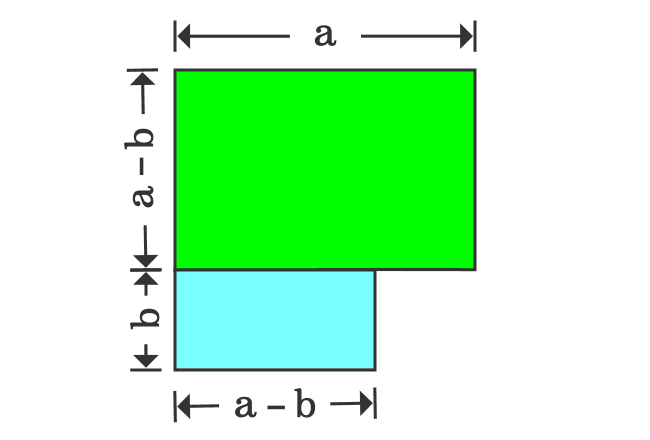


Proof Of A B Formula In Geometric Method


Using The Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Inequality In Problem Solving
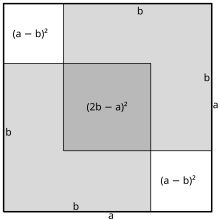


Square Root Of 2 Wikipedia



Inequality Of Arithmetic And Geometric Means Wikipedia
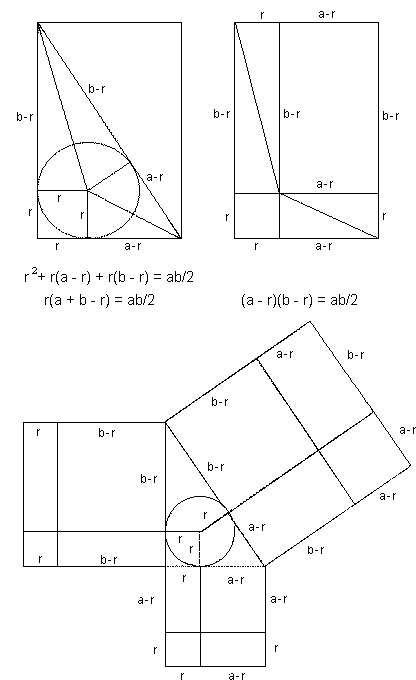


Pythagorean Theorem And Its Many Proofs



A Cube Minus B Cube A 3 B 3 Geometrical Explanation And Derivation Of Algebra Identity Youtube



Introduction To Proofs Read Geometry Ck 12 Foundation


Pythagorean Theorem Wikipedia



A B 3 3d Visual Proof Geometric Proof A Plus B Whole Cube Class 9 Algebraic Identity Youtube



Pythagorean Theorem And Its Many Proofs
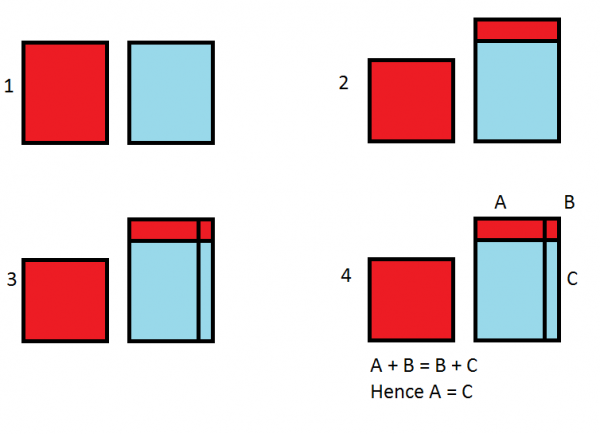


Do These Glasses End Up With The Same Amount Of Each Type Of Soda The Reflective Educator
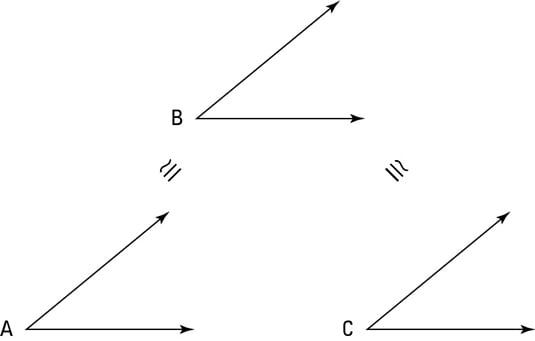


The Transitive And Substitution Properties Dummies



Firststep By Rishabh Singla Geometrical Visual Proof Of The Famous Formula A B 2 A 2 B 2 2 A B
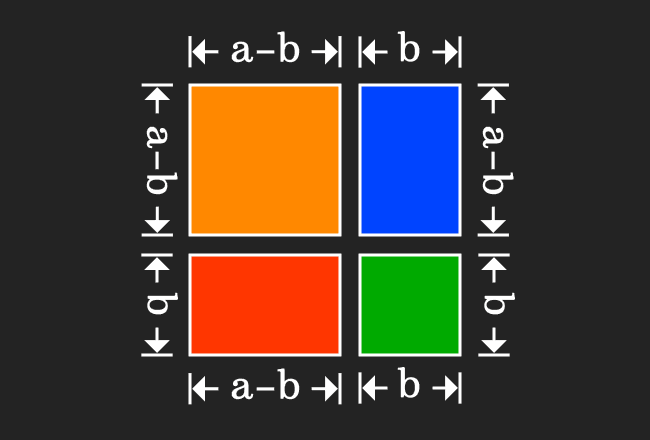


Proof Of A B Formula In Geometric Method


Illustrations Of Formulas


What Are The Best Examples Of Mathematical Proofs Without Words Quora


Kttmc Weebly Com Uploads 2 1 2 7 2 6 D2 Proof Worksheet 3 Pdf



A Geometric Proof For Sin A B Sinacosb Sinbcosa Ppt Download


Http Www Berkeleycitycollege Edu Wp Wjeh Files 13 01 Geometry Note Summary Theorems Pdf



Art Of Problem Solving
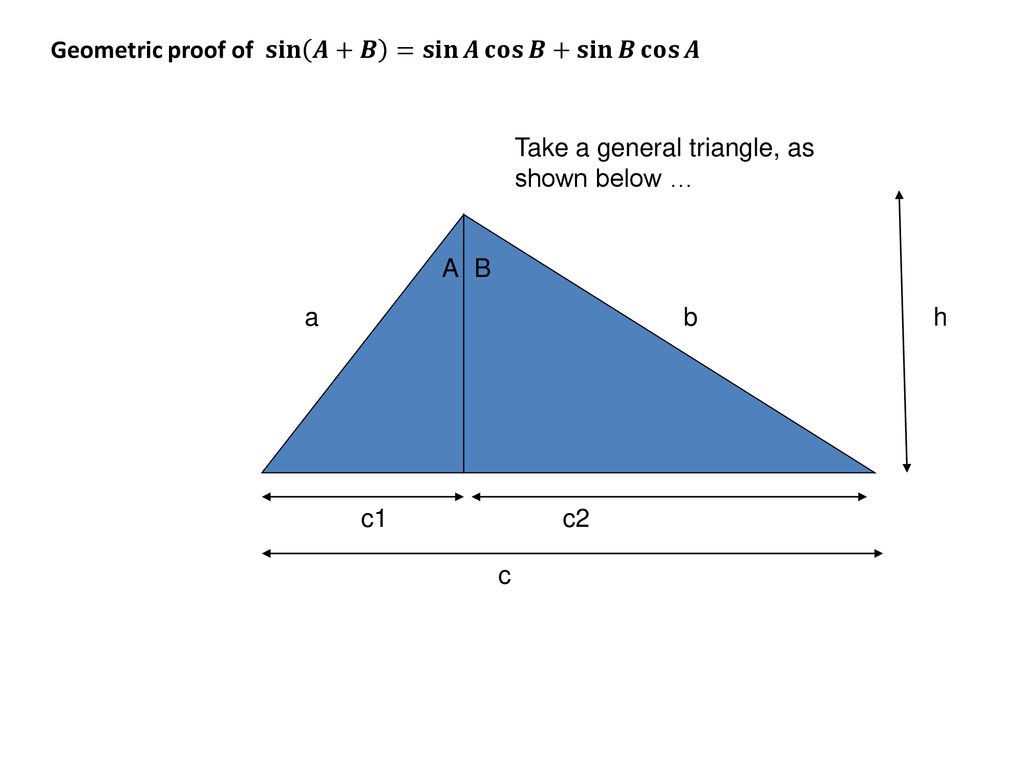


Trig Addition Formulae Ppt Download
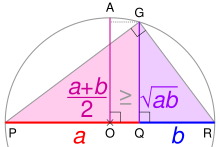


Inequality Of Arithmetic And Geometric Means Wikipedia
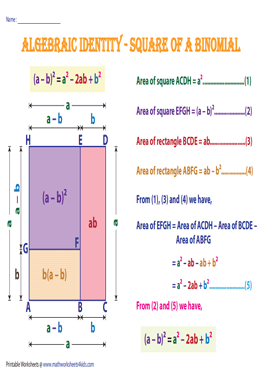


Algebraic Identities Charts Printable Formulas
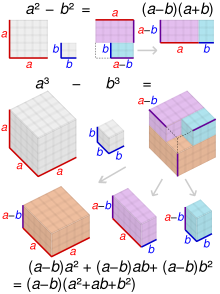


Difference Of Two Squares Wikipedia



How Should I Prove A B 3 A 3 3ab A B B 3 Model Or Figure Mathematics Stack Exchange



How To Prove That Lim Limits X To0 Frac Sin X X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Good Math Problems Continuous Everywhere But Differentiable Nowhere Page 7


2 6 Geometric Proof Themath



A B 3 Geometrical Proof Youtube



A B 3 I E A Plus B Cube Formula Proof Ntse Algebraic Formulas Identity Geometrically Youtube



ℵm B ℝ ℏ G A Beautiful Geometric Visualization Of



Yismxplusc Geometric Proof Of The Cubic Formula A B 3


Q Tbn And9gcq4zpmdaslfjtbs6yv7d6jfr01ay6awvv Z5riovxkoujojjcff Usqp Cau



Two Column Proof Guide W 7 Step By Step Examples



Geometric Proofs Of Trigonometric Identities Random Walks


Geometry Proofs Worksheets With Answers Kids Activities
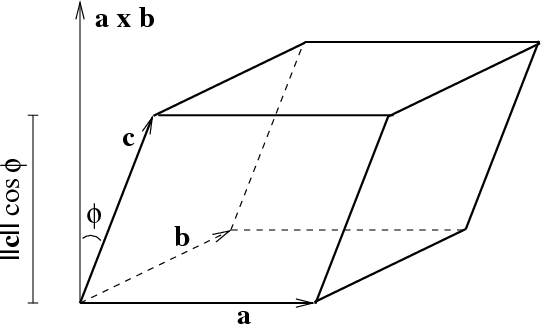


The Scalar Triple Product Math Insight



Chapter Activity Plus In Mathematics 9



Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab


Difference Of Cubes Math Central



Difference Of Two Cubes


コメント
コメントを投稿